In the Skin Stem Cell Team, we focus on the epidermal stem cells and their behaviors. We conduct research on inflammatory skin diseases including psoriasis, skin cancer, wound healing, and aging. Additionally, we are working on elucidating the pathology and developing treatments for rare and intractable diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa and pachyonychia congenita. Faculty members Ken Natsuga, Mika Watanabe, Shota Takashima, and Takuya Maeda are the group leaders of this team.
Major research results since 2017
-
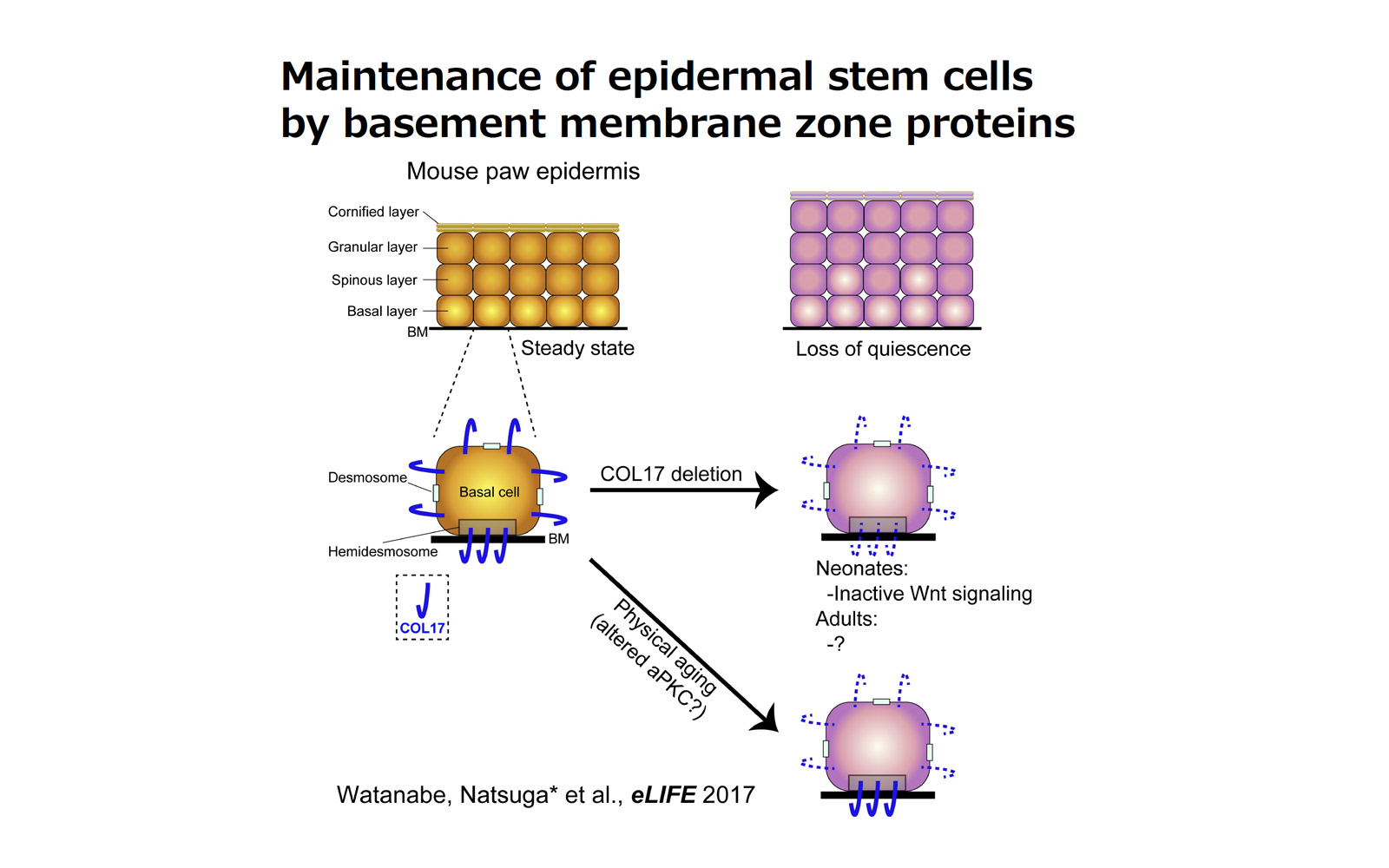
Type XVII collagen coordinates proliferation in the interfollicular epidermis (Watanabe, Natsuga et al. eLIFE 2017)
-
Loss of interaction between plectin and type XVII collagen results in epidermolysis bullosa simplex (Natsuga et al. Hum Mutat 2017)
-
Efficient gene reframing therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa with CRISPR/Cas9(Takashima, Shinkuma et al. J Invest Dermatol 2019)
-
Extramammary Paget’s disease patient-derived xenografts harboring ERBB2 S310F mutation show sensitivity to HER2-targeted therapies(Maeda, Yanagi et al. Oncogene 2020)
-
Type XVII collagen interacts with the aPKC-PAR complex and maintains epidermal cell polarity(Watanabe, Natsuga et al. Exp Dermatol 2021)
-
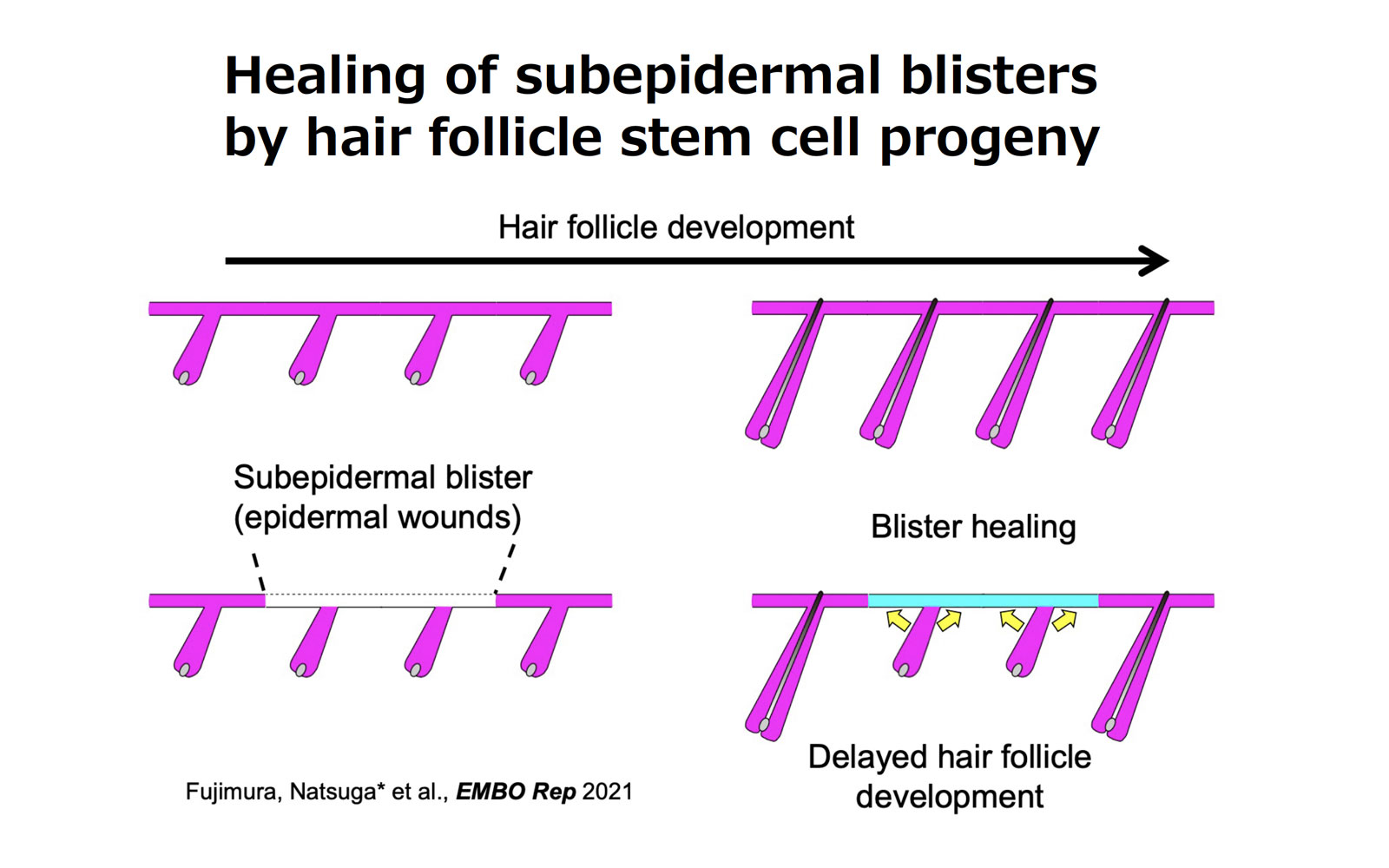
Hair follicle stem cell progeny heal blisters while pausing skin development (Fujimura, Natsuga et al. EMBO Rep 2021)
-
Wnt/β-Catenin signaling stabilizes hemidesmosomes in keratinocytes (Kosumi, Natsuga et al. J Invest Dermatol 2022)
-
Collagen XVII deficiency alters epidermal patterning (Wang, Natsuga et al. Lab Invest 2022)
-
Detection of revertant mosaicism in epidermolysis bullosa through Cas9-targeted long-read sequencing (Natsuga, Furuta et al. Hum Mutat 2022a)
-
Cas9-guided haplotyping of three truncation variants in autosomal recessive disease (Natsuga et al. Hum Mutat 2022b)
-
Patterning in stratified epithelia depends on cell-cell adhesion(Mai, Natsuga et al. Life Sci Alliance 2024)
<Major research achievements of the group leaders at institutes other than Hokkaido University>
- Increased bacterial load and expression of antimicrobial peptides in skin of barrier-deficient mice with Reduced Cancer Susceptibility (Natsuga, Watt et al. J Invest Dermatol 2016)
- Tissue memory relies on stem cell priming in distal undamaged areas(Levra Levron†, Watanabe†, Proserpio†, Donati et al. Nat Cell Biol 2023; †co-first authors)
- Alternative mRNA splicing events and regulators in epidermal differentiation(Takashima, Sun et al. Cell Rep 2024)
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with survival and sentinel lymph node positivity in invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective study(Maeda, Yoshino et al. J Am Acad Dermatol 2022)